Welcome to the Open Research Data Portal.
The ORD Portal is a collaborative effort to implement Open Research Data in the ETH Domain. Gain insight into ORD projects, find services supporting ORD practices and training.
Projects
RDS Explorer
Training
Documents
Open Research Data Projects in Focus
WSL
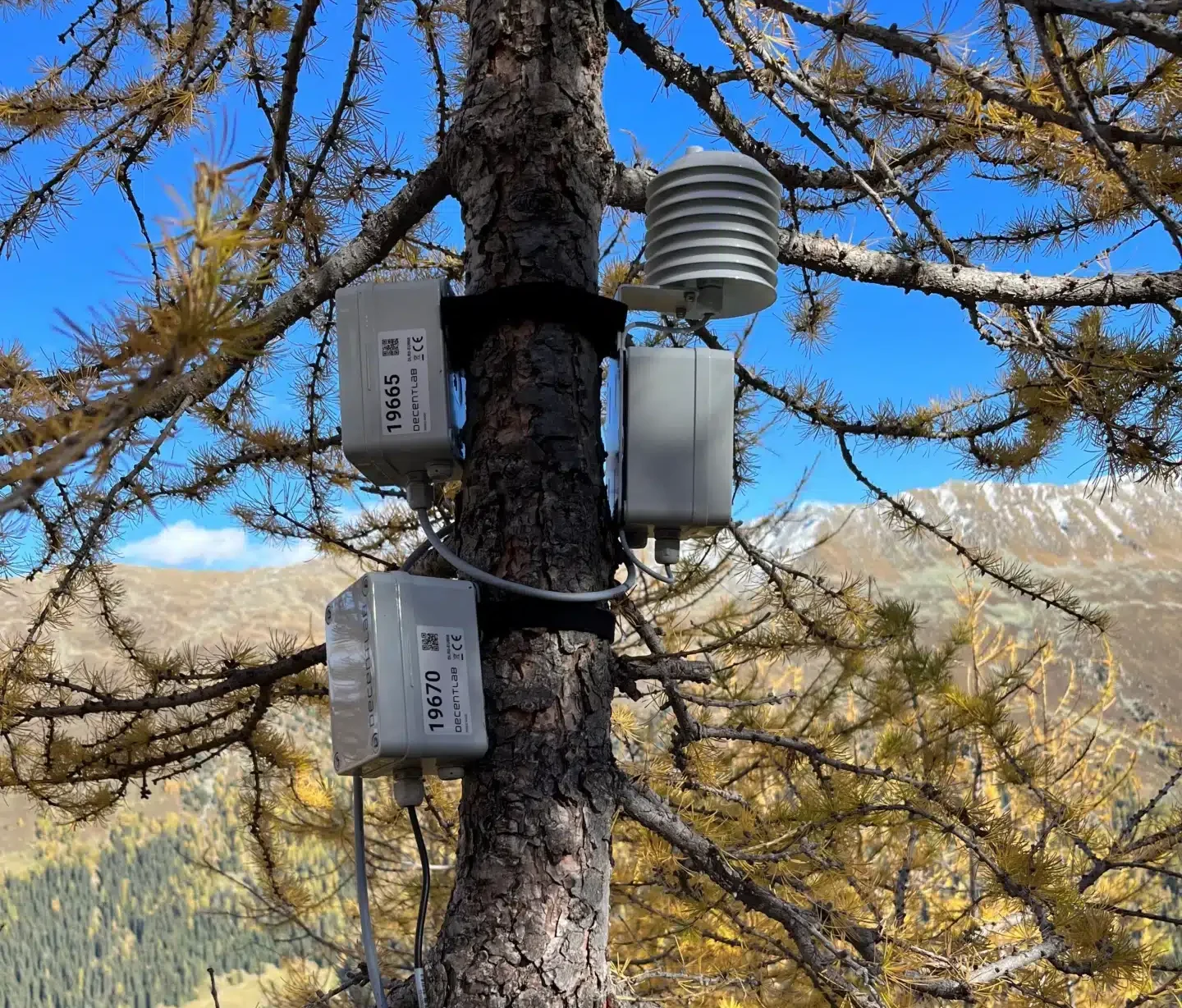
In a recent WSL research project (deepT - internal grant no. 202011N2099), a machine learning model was developed for gap-filling multi-channel time series data. The goal is to incorporate this model into the automated near real-time TreeNet data acquisition infrastructure. This addition will allow TreeNet dendrometer data users to fill time series gaps automatically using artificial intelligence.
ETH Zurich, Empa, PSI
This project seeks to promote and establish FAIR ORD practices in Materials Science, with a focus on streamlining the treatment of experimental and simulation data on the same footing. Metadata standards for interoperability between electronic lab notebooks (ELNs)/lab information management systems (LIMSs) and workflow management systems (WFMSs) will be developed in the field of Materials Science, and combined with ontological semantic annotations. Best practices for integrating ORD into the research process will be collected, designed, and disseminated. Pilot use cases (focusing in particular on microscopies, spectroscopies, and battery research) that are applicable broadly to Materials Science research will demonstrate the deliverables. Open platforms like openBIS and AiiDA+AiiDAlab will be enhanced to meet FAIR requirements. These advancements will enable seamless interoperability between ELN/LIMS and WFMS. The ultimate goal of the project is to contribute to autonomous laboratories, where AI-driven simulations and robotic experiments expedite materials discovery and characterization.
See the website: https://ord-premise.org/
ETH Zurich, EPFL, Empa, PSI, with swissuniversities partners UNIGE, UNIBE, UNIBAS, UNIL
The Open EM Data Network (OpenEM) in Switzerland will implement ORD practices for Electron Microscopy (EM). Cryo-EM has revolutionized protein structure determination, while materials science has seen a surge in possibilities, including 4D STEM data. This has led to increased data volumes and computational needs. OpenEM will extend PSI’s SciCat Data Catalog to provide open and FAIR access to EM data Swiss-wide. It aims to standardize data and metadata collection, streamline acquisition, facilitate data sharing, automate deposition in international ORD repositories, offer user training, and establish a sustainable structure beyond the project’s closure. A parallel initiative through the swissuniversities CHORD program funds the participation of partners outside the ETH domain. OpenEM complements the “EM frontiers” initiative to advance electron microscopy technology in Switzerland, included in the Swiss Roadmap for Research Infrastructures 2023. See the website: https://swissopenem.github.io/
ETH Zurich
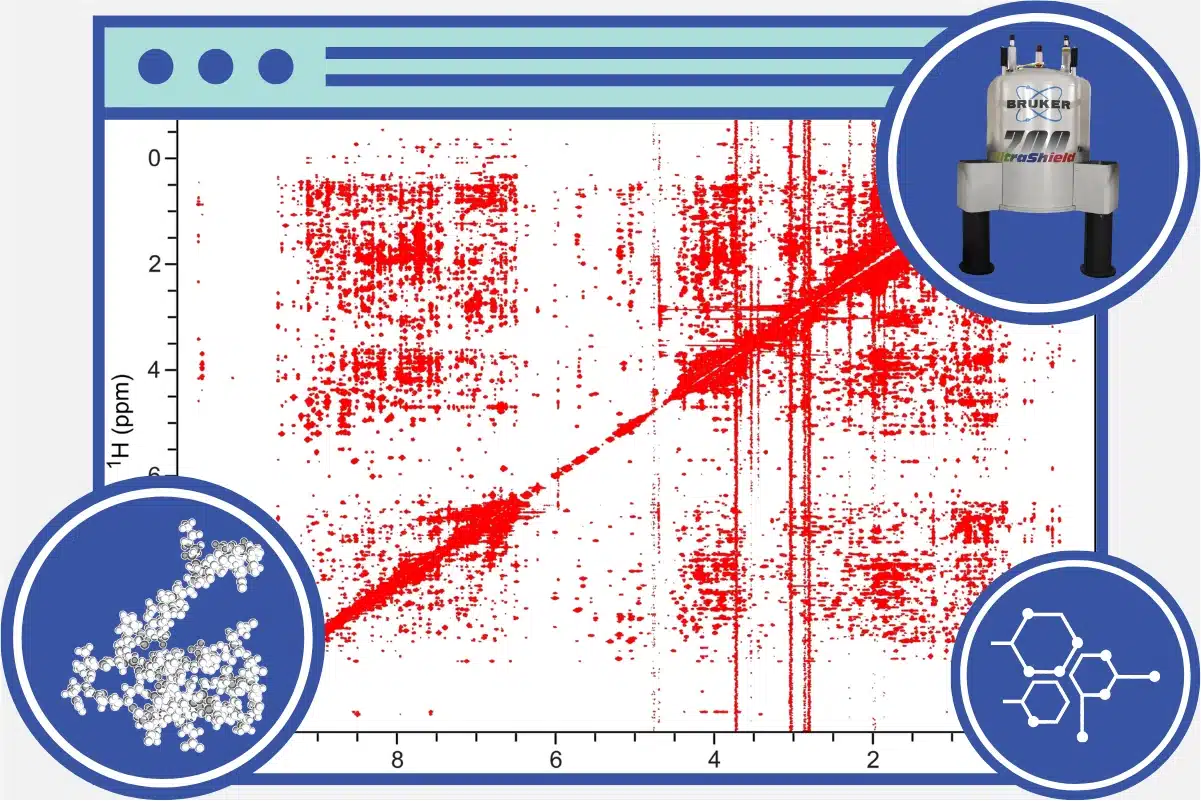
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, vital in structural biology, lacks an open database for primary data – multidimensional NMR spectra. These spectra are fundamental for in-depth protein analysis but remain largely inaccessible. The NMRprime initiative seeks to establish a FAIR-compliant database, integrating with the Protein Data Bank (PDB) and Biological Magnetic Resonance Bank (BMRB). NMRprime will facilitate spectrum uploads, automated annotation via machine learning, search capabilities, and open data access. The goal, in collaboration with PDB, BMRB, and journals, is to mandate NMR spectra deposition for bio-NMR projects, paralleling protein structure deposition in the PDB as is well-established for other methods in structural biology such as X-ray crystallography. NMRprime's expertise in bio-NMR and automated spectral analysis makes it the ideal candidate for this mission.